You have no items in your shopping cart.

Zero Trust Security for Schools: A Complete Guide
With the rise of online learning and increasing reliance on technology, schools, and universities are becoming prime targets for cyber threats.
Traditional security models, like the "castle-and-moat" approach, are no longer sufficient for securing today's complex educational environments. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), introduced by John Kindervag in 2010, offers a comprehensive solution by continuously verifying and authenticating every user and device, whether inside or outside the network, before granting access.
In this article, we’ll cover how Zero Trust protects sensitive information, ensures regulatory compliance, and defends against growing cyber threats in education. You'll learn about its key pillars and why it's crucial for student data privacy and network security in modern educational institutions.
Understanding Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a cybersecurity framework that operates on the principle of never trust, always verify. In contrast to traditional models, where users and devices within the network are implicitly trusted, Zero Trust requires continuous verification and strict access control at every point.
This is particularly essential for educational institutions handling vast amounts of sensitive student data and research materials.
With Zero Trust for schools, each access request—whether from students, staff, or external users—is authenticated, authorized, and evaluated in real-time. This framework also integrates continuous monitoring to detect and respond to potential cyber threats proactively.
Top Reasons Schools Need Zero Trust Security
1. Securing Open and Dynamic School Networks
Schools and universities host a diverse range of users, including students, faculty, researchers, and external partners.
These users constantly connect and disconnect from the network, creating an open and dynamic environment that is highly vulnerable to cyberattacks. Traditional security models often rely on broad access permissions, which expose institutions to cyber threats.
Zero Trust Security ensures that every connection is authenticated in real time, preventing unauthorized access.
Whether users are on campus or accessing the network remotely, this architecture provides secure remote access for schools and protects critical resources from being compromised.
2. Increased Cybersecurity Threats Facing Schools Today
- Target for Cyberattacks: Universities and schools are often targeted for cyberattacks because they store sensitive data such as student records, financial information, and valuable research data. The increasing incidents of ransomware and phishing attacks highlight the importance of having a security model that assumes any user or device could be compromised.
- Insider Threats: Whether intentional or accidental, insider threats pose a significant educational risk. Zero Trust mitigates potential damage by enforcing least-privilege access and continuously monitoring all users and devices.
3. Protecting Sensitive Student Data
Schools must comply with strict data protection regulations, such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) in the U.S. and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
These regulations require that student data privacy be maintained and that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
Zero Trust helps schools enforce data encryption both at rest and in transit. By segmenting network access and applying role-based permissions, Zero Trust ensures that only authorized personnel can view or manipulate sensitive student data, significantly reducing the risk of breaches.
4. Zero Trust for BYOD and Remote Learning in Education
- Remote and Hybrid Learning: The rise of online and hybrid learning models, particularly after the pandemic, has broadened the potential for cyber-attacks. Zero-trust security measures validate users and devices for remote connections, regardless of their location.
- BYOD Challenges: Students and staff use personal devices to access institutional resources, so securing these devices becomes challenging. Zero Trust addresses this by continuously evaluating the security posture of each device before granting access.
How to Implement Zero Trust in Schools for BYOD Security:
- Device Posture Checks: Schools should ensure that all devices meet security requirements, including up-to-date operating systems and active antivirus protection.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): Using MDM solutions allows schools to enforce security policies on personal devices, ensuring compliance with regulations and protecting student data.
- Continuous Monitoring: Monitor devices continuously to detect changes in their security posture. This prevents compromised devices from accessing sensitive resources.
- Secure Remote Access: Use Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and VPNs to secure remote connections, ensuring both users and devices are authenticated before gaining access.
5. Zero Trust in Complex School IT Environments
Educational institutions often operate with a mix of legacy systems and modern cloud-based applications. Managing security across such a diverse environment can be challenging with traditional models.
Zero Trust provides a flexible security framework that applies consistent access policies across both on-premises and cloud environments.
Zero Trust simplifies the security management of complex IT environments by ensuring that all systems, regardless of age or location, are protected under the same set of security rules.
6. Managing Network and Application Access
- Granular Access Controls: Traditional access controls often depend on broad permissions according to user roles. Zero Trust enables educational institutions to establish more precise access controls, ensuring that users only have access to the specific resources they require and nothing more.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Threat Detection: Continuous monitoring and behavioral analytics help identify real-time anomalies, enabling faster detection and response to potential threats.
7. Scaling Security for Evolving Educational Needs
The security needs of schools are constantly evolving as they adopt new technologies and expand their digital infrastructures.
Zero Trust Security offers a scalable solution that adapts to these changes, allowing institutions to adjust security policies as new applications are introduced or remote learning models expand.
Zero Trust continuously verifies user identities and devices to ensure that schools remain secure even as their IT environments evolve.
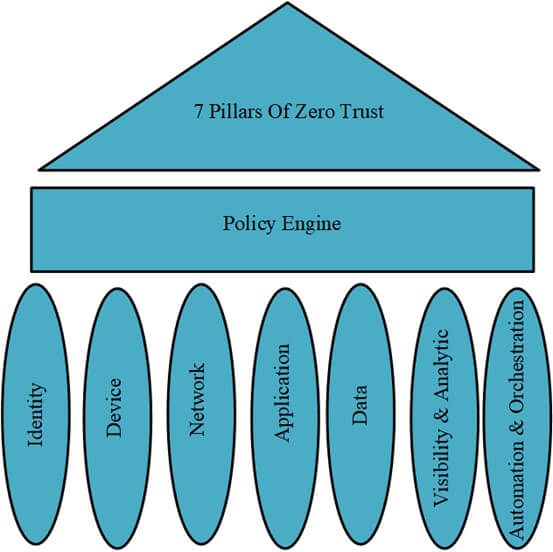
Zero Trust Security Framework: Key Pillars
1. Identity Verification
Identity verification is the cornerstone of Zero Trust Security. Schools must ensure that every user—whether student, staff, or external partner—has their identity verified before gaining access to any resource.
Key Practices:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requires multiple verification forms to prove identity, reducing reliance on passwords alone.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Ensures that users have access only to the resources necessary for their role.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Manages user identities and controls resource access, integrating with directories like Active Directory (AD) or Azure AD.
2. Device Protection and Management
Every device connected to the network must meet the institution’s security standards. Device posture assessments verify that devices are properly secured with up-to-date patches, antivirus protection, and encryption.
Schools can also use Mobile Device Management (MDM) to enforce security policies on personal devices, helping protect student data privacy.
3. Network Microsegmentation
Microsegmentation divides the network into smaller, isolated segments, each with its security controls. This limits attackers' ability to move laterally within the network.
By restricting access to specific areas of the network, Zero Trust minimizes the impact of potential breaches and helps ensure data privacy in education.
4. Securing Applications and Workloads
In a Zero Trust model, applications and workloads must be secured by controlling access and continuously monitoring their behavior.
Application Access Control ensures that only authenticated and authorized users can interact with sensitive applications, while Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) helps safeguard applications during execution.
5. Protecting Sensitive Data
Educational institutions handle large amounts of sensitive data, including student records and research.
Zero Trust ensures that this data is encrypted both at rest and in transit. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools also monitor the movement of sensitive information to prevent unauthorized access or leaks.
6. Visibility and Continuous Monitoring
Schools need complete visibility into all network activity to maintain a Zero Trust approach.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems aggregate and analyze data across the network, while User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) identify unusual behavior that could signal a potential breach.
7. Automation and Orchestration
Automation is crucial for maintaining security at scale. Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) automates the detection and response to threats, reducing the time it takes to address security incidents.
By automating policy enforcement, schools can ensure that their security measures remain effective and up to date.
Best NGFWs for Zero Trust in Schools
1. Palo Alto Networks: Advanced Threat Prevention
Palo Alto provides identity-based security and advanced threat prevention. Their Prisma Access and Prisma Cloud platforms extend Zero Trust to cloud environments and remote users.
- Zero Trust Focus: Palo Alto Networks leads in Zero Trust, offering robust identity-based policies, segmentation, and threat detection.
- Comprehensive Application Control: Palo Alto’s Application-ID feature can identify and control traffic for over 3,000 applications, helping us manage educational and non-educational apps, such as gaming or streaming.
- User-Based Policies: The firewall can enforce policies based on users and devices, which is vital in environments with diverse users, such as students, faculty, and staff, using different devices.
- Recommended Models: PA-220 for small campuses, PA-820 or PA-850 for medium-sized institutions, and PA-3400 series for large universities.
2. Fortinet: Cost-Effective, High-Performance Security
Fortinet’s FortiGate NGFW offers cost-effective Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and scalable VPN capabilities, making it ideal for schools with limited budgets.
- Cost-Effective: FortiGate NGFW provides excellent price-performance ratios, making it accessible for schools and universities with limited budgets.
- Comprehensive Security: It includes built-in Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) features, application control, web filtering, and deep packet inspection, which are critical for protecting against ransomware, phishing, and unauthorized access, common in academic settings.
- Scalability: FortiGate provides scalable VPN and SD-WAN capabilities for remote access in large, distributed environments such as campuses.
- Integration with Fortinet Solutions: It seamlessly integrates with FortiAuthenticator for identity management, FortiClient for endpoint protection, and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA).
- Recommended Models: FortiGate 100F or 200F for mid-to-large campuses, FortiGate 60F for smaller schools.
3. Cisco Firepower: Strong Identity Management and Network Visibility
Cisco Firepower integrates with Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) to enforce identity-based access controls and monitor network activity.
- Advanced Security Features: Cisco Firepower provides vital threat intelligence through Cisco Talos, intrusion prevention (IPS), and malware protection, making it well-suited for securing academic data.
- Network Visibility: Cisco Firepower’s deep integration with Cisco ISE provides excellent control over who can access which resources. This level of control is essential in a multi-user, multi-device environment such as schools and universities.
- Identity and Access Management: With Cisco ISE and Duo integration, Firepower provides strong identity management and MFA, ensuring secure access to necessary resources for students and staff.
- Education-Specific Features: Cisco offers customized solutions, including grants and pricing models, designed specifically for the education sector.
- Recommended Models: Cisco Firepower 1000 series for smaller institutions, Firepower 2100 series for more prominent universities.
Summary
Several brands provide strong Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs), essential components of a Zero Trust Architecture.
These NGFWs incorporate advanced threat prevention, identity management, and secure access controls, allowing organizations to implement a complete zero-trust strategy across their networks, applications, and data.
The right solution choice depends on your organization's specific needs, including the scale of deployment, integration requirements, and existing IT infrastructure.
Other vendors, such as Sophos, also offer comprehensive solutions for ZTA.
Conclusion: Implementing Zero Trust for the Future of Education
Educational institutions are facing increasingly complex cyber threats, and traditional security models are no longer sufficient.
Zero Trust Architecture offers a comprehensive and scalable solution, protecting sensitive student data, ensuring regulatory compliance, and securing both on-campus and remote learning environments.
By adopting Zero Trust for education, schools can safeguard their networks, protect student data, and ensure a safer, more secure future for students and staff alike.
To build a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy for your school or university, explore our related articles on safeguarding educational institutions:
- Cybersecurity in Education: Setup & Protection Plan
- Discover the key steps for creating a robust cybersecurity protection plan tailored for schools and universities. Learn how to establish foundational security measures that work in harmony with Zero Trust principles.
- 2024’s Best Cybersecurity Solutions for K-12 & Universities
- Find out the best cybersecurity tools and technologies available in 2024 for K-12 schools and universities. These solutions can complement your Zero Trust Architecture, ensuring complete protection against modern threats.






